Basic rules for calculation of energy and financial savings within the EURONET 50/50 MAX project:
- Energy and financial savings should be calculated after each year of the 50/50 implementation in school or other public building.
- The calculation should be done following the simple methodology described in point “Calculation methodology step by step”.
- Energy savings are calculated by comparing the energy consumption in the current year with the reference value, calculated as described in point “Calculation of reference values”
- Reference values remain the same for the whole project duration.
- Financial savings are calculated using energy prices valid in the current year.
Calculation methodology step by step:
The methodology of calculation of energy and financial savings is very simple:
- First – gather necessary data: you need energy bills, average prices of energy and degree days to reduce the impact of outside temperatures on energy consumption.
- Second – calculate electricity savings: in order to calculate electricity savings subtract the consumption of the current year from the consumption in a year preceding the implementation of the 50/50 methodology. The resulting saved KWh are multiplied by the average price of energy supply of the current year.
- Third – calculate heating savings: to calculate savings on heating we also compare the energy consumption with the reference period but in this case we need to adjust the consumption on heating with the heating degree days1. In this way we can lower the yearly differences of external temperature in heating consumption (the colder the weather, the more we spend on heating).
Calculation of reference values:
The calculation of reference values may seem a bit difficult at a first glance, but it is really not! Please follow the guidelines below:
- Calculation of reference value for heat:
In case of heat the reference value is calculated on the basis of average standardized energy consumption over the three years preceding the implementation of the 50/50 methodology:
- STEP 1 – calculation of standardized heat/fuel consumption for 3 following years preceding implementation of the 50/50 methodology:
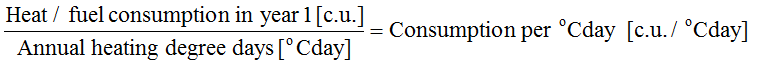 where: C.U. = Consumption Unit
where: C.U. = Consumption Unit - STEP 2 – calculation of average standardized heat/fuel consumption over the three following years:
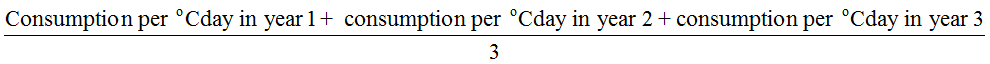
- STEP 3 – calculation of the reference value (reference consumption) to which the consumption in the current year (year A of the project) will be compared:
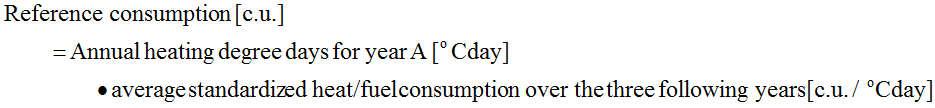
- STEP 1 – calculation of standardized heat/fuel consumption for 3 following years preceding implementation of the 50/50 methodology:
- Calculation of reference value for electricity
In case of electricity, the calculation of the reference value is more simple. You may simply use the energy consumption in the year preceding implementation of the 50/50 methodology. However, to be more precise, it is better to use the average value for the three following years preceding the project.
Exemplary spreadsheet to monitor energy consumption at school
[1] "Heating degree days", or "HDD", are a measure of how much (in degrees), and for how long (in days), outside air temperature was lower than a specific "base temperature" (or "balance point"). They are used for calculations relating to the energy consumption required to heat buildings. (Source: http://www.degreedays.net/)













 Η ευθύνη για το περιεχόμενο του παρόντος ιστοτόπου βαρύνει αποκλειστικά τους συντάκτες του και δεν απηχεί κατ’ ανάγκη την άποψη της Ευρωπαϊκής Ένωσης. Η ΕACI και η Ευρωπαϊκή Επιτροπή ουδεμία ευθύνη φέρουν για οποιαδήποτε χρήση των πληροφοριών που περιλαμβάνονται στον παρόντα ιστότοπο.
Η ευθύνη για το περιεχόμενο του παρόντος ιστοτόπου βαρύνει αποκλειστικά τους συντάκτες του και δεν απηχεί κατ’ ανάγκη την άποψη της Ευρωπαϊκής Ένωσης. Η ΕACI και η Ευρωπαϊκή Επιτροπή ουδεμία ευθύνη φέρουν για οποιαδήποτε χρήση των πληροφοριών που περιλαμβάνονται στον παρόντα ιστότοπο.